Turmeric Pests – Shoot borer: Adults are medium sized moths with pale yellowish wings consisting of black spots. The female moths lay eggs singly or in group on the tender parts of the plant. Larvae is long, pale greenish with a pinkish was dorsally, head and pro-thoracic shield brown in colour and body covered with minute hairs arising onwards. Pupation takes place in lose silken cocoon in larval tunnel. symptoms of damage include Yellowing and drying of leaves of infested pseudo stems. The presence of a bore-hole on the pseudo stem through which frass is extruded and the withered and yellow central shoot. Growth of the plant become stunted.
Management: Immediately after noticing the infestation apply Neem cake powder 100kg/acre or apply lambda cyhalothrin granules 1ml/litre of water.
Rhizome scale: Female scales are circular (about 1mm diameter) and light brown to gray and appear as encrustations on the rhizomes. Male is orange coloured with transparent wings, distinct head, thorax and abdomen. Symptoms of damage are plant becomes pale, devitalized withered and devitalized. Plants look devitalized, pale and withered before drying completely. In such cases at the time of harvest minute yellowish crawlers can be seen moving in large numbers and this is the potential stage of dissemination. Storage infestation symptoms includes white-coloured scales scattered on rhizomes and later they congregate near the growing buds. When the infestation is severe the rhizome and buds shrivel and ultimately the entire rhizome dries.
Management: Discard and do not store severely infested rhizomes. Collect and destroy damaged leaves. Select healthy rhizomes free from scale infestation for seed materials. Treat seed material with quinalphos 0.075% (for 20-30 minutes) before storage and also before sowing in case the infestation persists. Apply well rotten sheep manure @ 10 t/ ha in two splits or poultry manure in 2 splits followed by drenching dimethoate 30 EC @ 2 ml or phosalone 35 EC @ 2ml /lit of water.
Also Read: Management of Pest Attack in Betel vine.!
Turmeric Pests
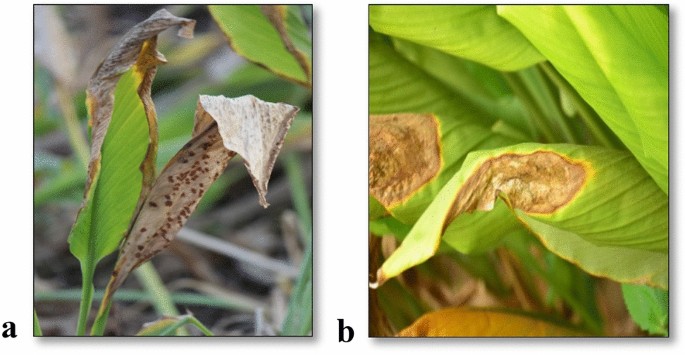
Thrips: Adults have elongated abdomen and are yellowish or blackish in colour. These are found on plants throughout all growth stages, from sprout development to tuber maturation. Favourable conditions for pest infestation is dry and weather conditions. Symptoms of damage include upward marginal curling of infested leaves as the nymphal stages suck the sap from under surface of the leaf. Also they damage young and soft parts of plants such as new leaves and shoots. Infested leaves become rolled up, and turn pale & gradually dry-up. Severe infestation causes young leaves to wilt and dry out.
Management: Collect and destroy the infected plant parts. Install sticky traps @ 20/acre in order to the monitor the pest population. spraying of Dimethoate @ 2ml or Thiomethoxam @ 0.5g or Acetamipirid 0.2g per liter of water can reduce the infestation of thrips.
Rhizome, Root rot: It is a soil borne and seed borne disease seen in all turmeric growing regions. The infected plants show yellowing of leaves starting from lower leaves which gradually spread to the upper regions of the plant. The margins of the yellowing leaves turn necrotic and start drying from the margins inwards resulting in partial or complete blighting of leaves. Water-soaked dark brown lesions appear on the pseudostems at the base which enlarge rapidly resulting in drying up. The affected pseudostems break away with a pull and the affected tillers topple off. The infection spreads from roots to rhizome causing soft rot.
Management: Removal and burning of the infected clumps from the field. Seed dip in metalaxyl 8 + mancozeb 72 (Ridomil MZ) at 2.5 g lit for 40 minutes and soil drenching (0.1 g/lit) not only controlled rhizome rot disease but also increased the rhizome yield. In the field immediately after seeing the initial symptoms of the disease. drenching the soil in root region with Mancozeb (75 WP) – 1500 g/ha or Captan (50 WP) – 1000 g/ha or Copper oxychloride (50 WP) – 1250 g/ha or Bordeaux mixture – 5000 g/ha.
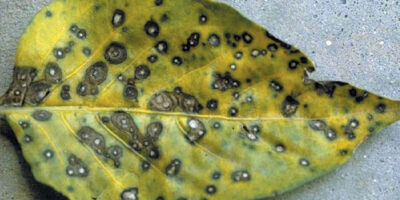
Leaf blotch (Taphrina leaf spot): It is a soil borne disease. The disease starts as small scattered oily looking translucent spots on the lower leaves when the plants are in 3 to 4 leaf stage. The leaf spots later turn dirty yellow and deepen to the colour of gold and sometimes to hay shade. The adjacent individual leaf spots of 1-2 mm in diameter coalesce forming reddish brown blotches leading to varying degrees of leaf blight. Owing to excessive spotting and destruction of chloroplasts, the functional laminal surface is considerably reduced resulting in indirect bad effect on the productivity of the plant.
Management: Field sanitation should be practiced. Crop rotation becomes important to reduce the inoculum build up. Spray carbendazim 1g or mancozeb 2.5g or propiconazole 1ml per litre of water 3-4 times at 15 days interval.
Also Read: Determination of Soil test for soil health.!