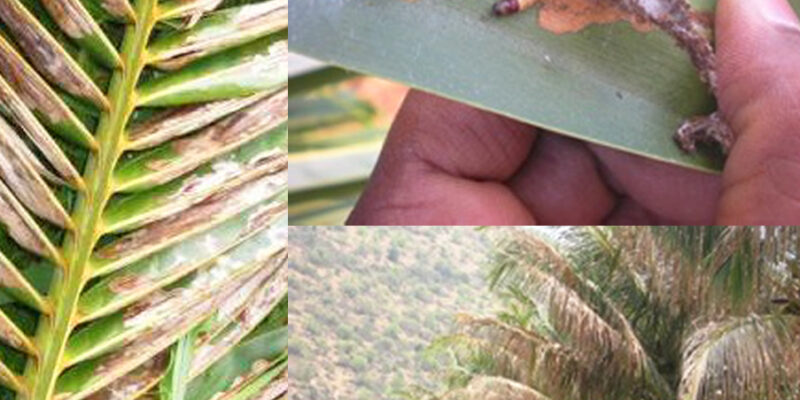
Black Headed Caterpillar: India ranks 3rd in the total coconut production of the world, contributing 34% to the global production. Ap contributes nearly 1,127.27 tonnes of total coconut production of India there by ranking 4th in position. The long-term life span of coconut will help to generate the income to the farmers even for decades. Coconut cultivated mainly in the coastal & backwater area of AP. With extreme changes in the weather condition the cultivation of coconut has become difficult because of the increased pest and diseases there by increasing the cost of cultivation. So, predicting the pest occurrence based on the weather phenomenon will helps to reduced the pest invasion.
One of the most devastating pests of coconut is Coconut Black Headed Caterpillar which affects the palm throughout the year at all ages. Extreme dry conditions are most favourable for the pest survival. It damages the leaf by feeding on the leaf tissue. The greyish white adult moth lays small eggs near the tip of the leaflets of the older leaves. Greenish brown larvae with dark head & prothorax and a reddish mesothorax emerges from the egg. Larval period lasts for 45 days. It completes pupation inside the galleries/silken tunnels.
The pupal period lasts for days. The total life cycle is completed within 2 months. The damage results in galleries/silken tunnels filled with frass and excreta on the underside of the leaves. The larvae feeds on the green parenchymatous tissues of leaflet from underside leaving a thin parchment like upper epidermis undamaged. The larval feeding results grey to brown leaflets which dries up in patches. In severe infestation the crown gives a scorched appearance. The pest infestation leads to severe yield loss to the farmers.
Also Read: Banana Burrowing Nematode: Burrowing nematode management in Banana
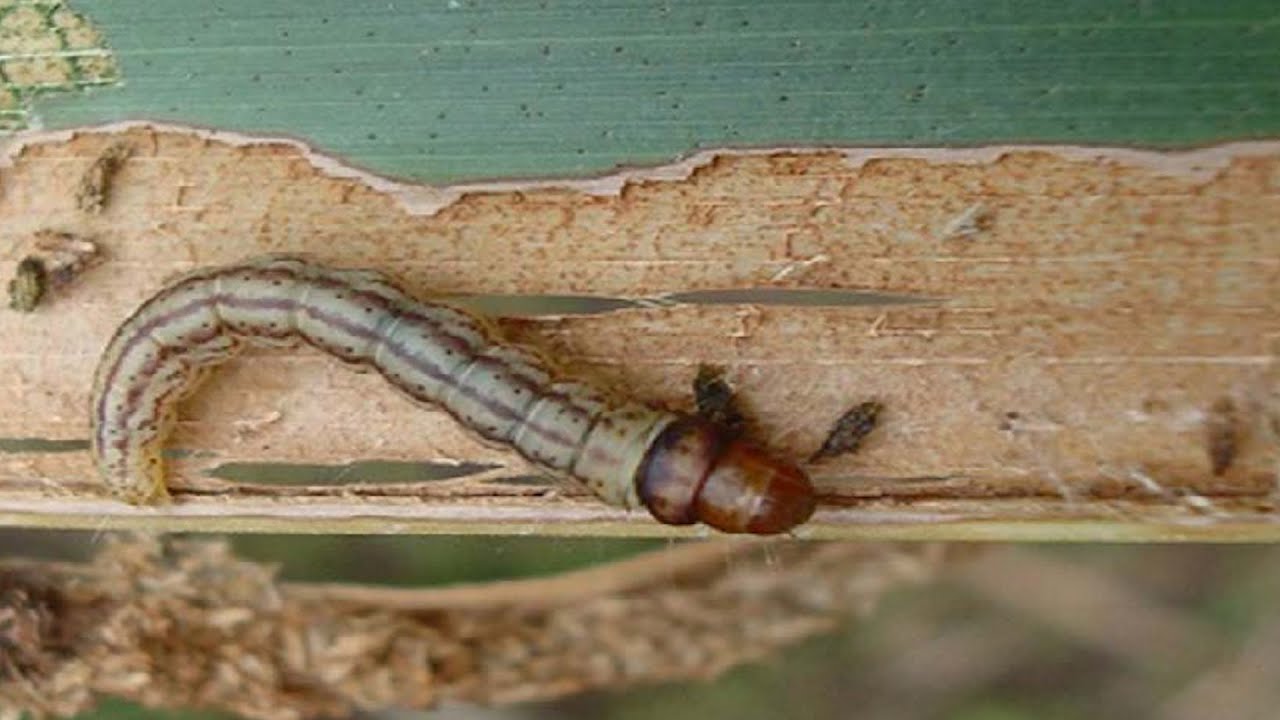

Black Headed Caterpillar
The primary management practice is to remove and burn all the pest affected leaflets. Then releasing of larval parasitoids Goniozus nephantidis @ 3000/ha will help in biological control of pest. The most important management practice followed for controlling coconut black headed caterpillar is stem injection & root feeding technique. During the root feeding technique, fresh and live roots are selected, then cut sharply at an angel and remove the excess part, then cover the root with polythene bag which consists of solution prepared by mixing monocrotophos 36 WSC+ water 10ml.
Air tight the polythene bag with a cotton thread and rest it for 24 hours, later check on the absorption of the root, if there is no absorption select another root and repeat the procedure. This technique is performed during severe outbreak of pest. Another important practice performed for controlling black headed caterpillar is stem injection. A slant downward hole is performed on the stem and injecting 5.0 ml of monocrotophos 36 WSC mixed in 20ml of water into the stem at about 1.5m above the ground level. Plug the hole with clay mixed copper oxychloride.
Before performing this technique, the nuts should be harvested. For the palms of age less than 10 years inject monocrotophos 5.0ml mixed in 20ml of water into the stem. The harvesting of tender nuts should be strictly avoided for 45 days after treatment. By following above briefed management practices farmers can reduce the infestation of coconut black headed caterpillar and thereby harvesting profitable yields.
Also Read: Rajendranagar: ICAR organized Strategic Planning Meet at Rajendranagar